WORLD electronics offers a complete line of electronic circuit board manufacturing and assembly services, as well as advanced manufacturing services. Our commitment to quality and service is second to no supplier.
Learn MoreOur team of engineers assists you in the development of new designs to optimize quality manufacturability (DFM) and testability, resulting in cost minimization and reduced product development time.
Learn MoreOur flexible manufacturing floor layout and highly trained staff allow for Quick Set-up and Tear Down of small volume prototype runs. This combination grants our customers the benefit of turning new designs quickly and accurately.
Learn MoreWORLD electronics is dedicated to quality. This quality is what underpins our commitment to thorough testing. Our engineers can develop a set of tests that ensure reliability and high performance in all products.
Learn MoreSupply chain management has crossed over from being a narrow management function to being a key operational function.
Learn MoreIn the evolving landscape of electronics manufacturing, electronic board assembly has become a pivotal focus for industries aiming to enhance productivity and maintain high-quality standards. According to a report by IPC – Association Connecting Electronics Industries, the global market for electronic assembly is projected to grow significantly, driven by the rising demand for advanced technologies and miniaturization in devices. As organizations strive to stay competitive in this fast-paced environment, mastering the nuances of electronic board assembly is crucial. Effective assembly practices can minimize defects and improve yield rates, which are vital for sustaining profitability in a sector where margins are increasingly tight.
However, achieving success in electronic board assembly is not without its challenges. With the complexity of modern circuit boards and the integration of diverse materials and components, manufacturers often encounter pitfalls that can lead to delays and increased costs. A study from Research and Markets highlights that nearly 30% of companies report issues stemming from inadequate quality control measures and inefficient assembly processes. By recognizing these common obstacles and implementing strategic solutions, companies can navigate the intricacies of electronic board assembly more effectively, ensuring that they not only meet but exceed industry standards. It's essential for manufacturers to adopt a proactive approach, leveraging best practices and innovative technologies to overcome these challenges and optimize their assembly processes.

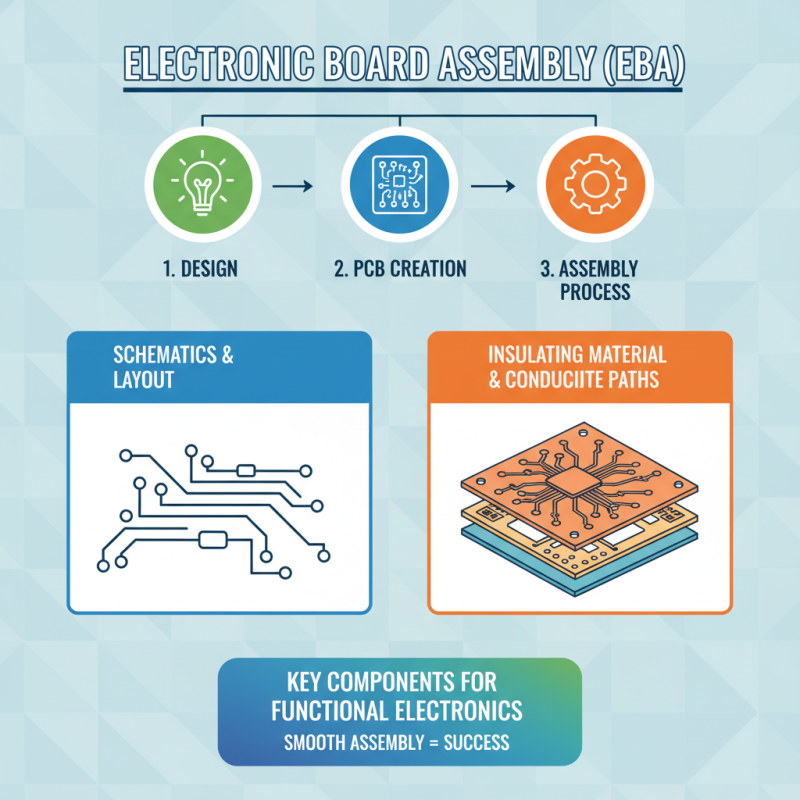
Electronic board assembly (EBA) is a crucial process in the manufacturing of electronic devices, encompassing various steps that transform raw materials into functional circuit boards. The initial phase involves designing the board, where engineers create schematics to specify the layout and interconnections of components. This is followed by creating the printed circuit board (PCB) itself, which is made from insulating materials with conductive pathways imprinted on the surface. Understanding these foundational components is essential for achieving a smooth assembly process.
Once the PCB is prepared, component placement begins. This step can use manual labor or automated equipment like pick-and-place machines to ensure precise positioning of components on the board. Following placement, soldering is performed to establish electrical connections, which can be achieved through various techniques such as wave soldering, reflow soldering, or hand soldering, depending on the design and application requirements. Awareness of these methods and their specific advantages is vital for ensuring high-quality assembly while minimizing defects and maximizing efficiency in the production line.
Efficient electronic board assembly relies heavily on the right components and tools, which can significantly streamline the production process. Key components such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits must be selected for compatibility with the intended application and performance specifications. A recent industry report indicates that choosing high-quality components can lead to a 15% reduction in assembly errors. It’s essential to invest in components that not only meet the technical requirements but also are sourced from reputable suppliers to ensure reliability and longevity.
In addition to choosing the right components, utilizing the appropriate tools is critical for a successful assembly. Soldering tools, inspection equipment, and mounting machines play an integral role in the precision and efficiency of the assembly process. The use of automated pick-and-place machines has been shown to increase production speed by up to 30%, enhancing overall throughput.
**Tips:** When selecting tools, prioritize those that offer versatility and ease of use. Regular maintenance of equipment is also crucial to avoid unforeseen downtimes, which can disrupt the assembly process. Furthermore, ensure that all team members are trained in using these tools effectively to maximize productivity and minimize common challenges associated with electronic board assembly. Keeping abreast of industry trends and advancements can also provide valuable insights into optimizing the assembly process.
| Component/Tool | Description | Common Challenges | Tips for Success |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soldering Iron | Used for joining electronic components by melting solder. | Overheating components, unclear connections. | Ensure proper temperature settings and tip condition. |
| PCB (Printed Circuit Board) | Base for mounting components. | Design flaws, layout issues. | Thorough review and testing of designs before fabrication. |
| Multimeter | Device for measuring voltage, current, and resistance. | Incorrect readings, user error. | Calibrate regularly and check connections before testing. |
| Tweezers | Used for handling small components. | Damaging components, poor grip. | Select the right type of tweezers for specific tasks. |
| Flux | Reduces oxidation during soldering. | Residue buildup, inadequate flow. | Use appropriate flux and clean after soldering. |

When it comes to electronic board assembly, several common challenges can hinder the production process and impact the quality of the final product. One prevalent issue is misalignment of components during soldering. This can lead to short circuits or unconnected parts, which ultimately affects the functionality of the board. To combat this, ensuring that the components are correctly placed before soldering is crucial. Utilizing automated pick-and-place machines can significantly reduce the risk of human error in alignment.
Another challenge is thermal management during the soldering process. Excessive heat can damage sensitive components, while insufficient heat may result in poor solder joints. Implementing proper heat profiling techniques can help manage temperatures effectively, ensuring that components are neither overheated nor underheated. Additionally, using thermally conductive materials can help distribute heat evenly across the board.
To optimize the electronic board assembly process, it is beneficial to conduct regular inspections throughout production. This fosters early detection of defects, ensuring that any errors are rectified promptly, which can save both time and resources. By focusing on these common challenges and applying targeted solutions, manufacturers can improve their assembly processes and enhance the reliability of their electronic products.
Quality control in electronic assembly is crucial for ensuring the longevity and reliability of the final product. To achieve high standards, it's essential to implement a rigorous quality management system from the outset. This includes defining clear specifications for components and processes, which helps in minimizing misunderstandings and errors during assembly. Regular calibration of machinery and tools is also vital to maintain precision in soldering and placement processes. Employing automated inspection systems can enhance detection of defects early in the production cycle, reducing the risk of faulty products reaching consumers.
Additionally, fostering a culture of continuous improvement among team members can significantly enhance quality control efforts. Encouraging employees to identify and report issues not only empowers them but also leads to valuable insights for process optimization. Routine training sessions can keep the team updated on best practices and emerging technologies, ensuring that everyone is on the same page when it comes to quality standards. Documenting and analyzing failure rates and quality-related incidents can provide a roadmap for future improvements, making it easier to pinpoint areas that require attention. By prioritizing quality control in electronic assembly, manufacturers can significantly improve product reliability and customer satisfaction.
This bar chart illustrates the error rates at various stages of the electronic board assembly process. Key areas such as design review, component sourcing, assembly process, quality testing, and final inspection are highlighted, showing the importance of quality control in achieving successful electronic assembly.
Streamlining workflow in electronic board assembly involves a combination of strategic planning and effective resource management. One of the most crucial tips for enhancing efficiency is ensuring that all necessary components and tools are readily accessible before commencing the assembly process. Organizing workstations in a logical manner can significantly reduce time wasted searching for parts and tools. Implementing a standardized assembly procedure can also minimize variability in the process, fostering consistency and quality in the final product.
Another critical factor in minimizing errors lies in the training and skill level of assembly personnel. Investing in comprehensive training programs not only equips employees with the necessary skills but also instills a sense of ownership and responsibility for the quality of their work. Regularly inspecting components and conducting pre-assembly checks can help identify potential issues early, preventing mistakes from escalating during the assembly phase. Additionally, fostering open communication among team members encourages a collaborative environment where questions can be resolved quickly, further decreasing the likelihood of errors.