WORLD electronics offers a complete line of electronic circuit board manufacturing and assembly services, as well as advanced manufacturing services. Our commitment to quality and service is second to no supplier.
Learn MoreOur team of engineers assists you in the development of new designs to optimize quality manufacturability (DFM) and testability, resulting in cost minimization and reduced product development time.
Learn MoreOur flexible manufacturing floor layout and highly trained staff allow for Quick Set-up and Tear Down of small volume prototype runs. This combination grants our customers the benefit of turning new designs quickly and accurately.
Learn MoreWORLD electronics is dedicated to quality. This quality is what underpins our commitment to thorough testing. Our engineers can develop a set of tests that ensure reliability and high performance in all products.
Learn MoreSupply chain management has crossed over from being a narrow management function to being a key operational function.
Learn MoreNavigating the printed board assembly process can be a daunting task for beginners, given the intricate nature of electronics manufacturing and assembly. Printed board assembly (PBA) is a critical phase in the production of electronic devices, where components are mounted onto printed circuit boards (PCBs) to create functional units. For those just starting in this field, understanding the key stages of PBA is essential to successfully bringing their electronic designs to life.
In this guide, we will explore the fundamentals of printed board assembly, covering important topics such as design considerations, selection of components, and the various assembly techniques available. By breaking down the process into manageable steps, newcomers can build confidence and knowledge, ultimately leading to the successful execution of their projects. Whether you are an aspiring engineer, a hobbyist, or a student, grasping the essential elements of printed board assembly will equip you with the skills needed to thrive in the fast-paced world of electronics.
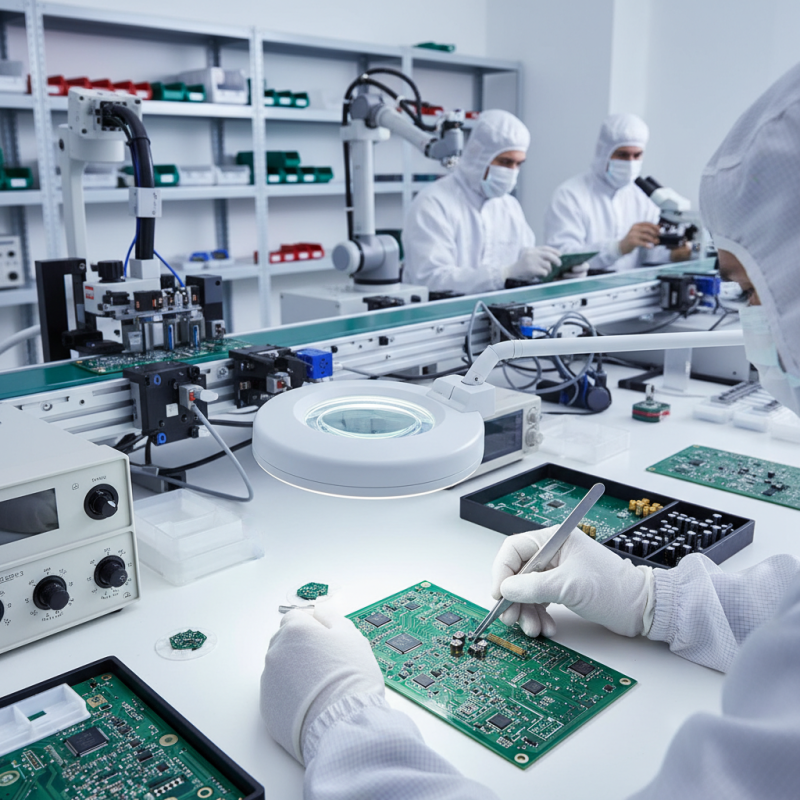

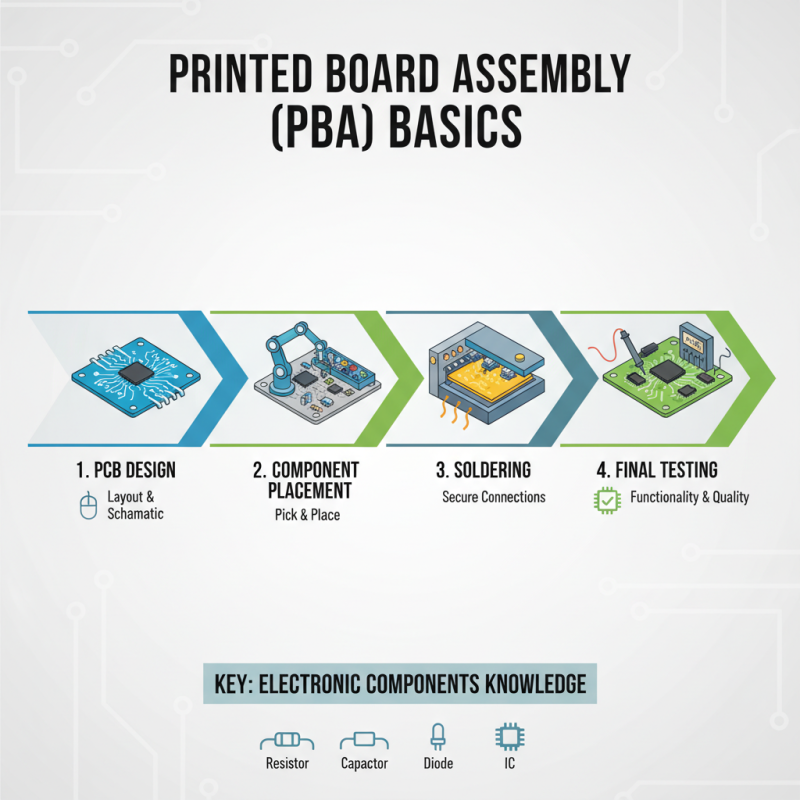
Understanding the basics of Printed Board Assembly (PBA) is essential for anyone looking to break into electronics manufacturing. PBA involves several key steps, including designing the printed circuit board (PCB), placing components, soldering, and final testing. A basic understanding of electronic components and their functions is critical, as it enables beginners to follow the assembly process more effectively.
Tips: Familiarize yourself with common electronic components, such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits. Recognizing these components and understanding their roles will streamline your assembly process.
When diving into the PBA process, it's crucial to prioritize quality and accuracy. The initial design phase plays an important role in determining the success of the assembly. Make sure to utilize design software that checks for common errors, as these can lead to complications during assembly.
Tips: Conduct thorough reviews of your designs and consider peer feedback to identify potential issues early on. This proactive approach can significantly enhance the quality of the final product.
When embarking on the journey of printed board assembly (PBA), having the right tools and equipment is crucial for beginners to achieve success and efficiency. Essential items include a soldering iron, solder, and a multimeter. A soldering iron allows you to join components securely to the printed circuit board, while solder provides the necessary conductive connection. A multimeter is vital for testing connectivity and ensuring proper voltage levels, helping you avoid costly errors.
Tips: Always use a soldering iron with adjustable temperature settings to prevent damage to sensitive components. Start with a small gauge solder to make your initial solder joints easier and cleaner.
Further enhancing your PBA experience requires a few additional tools, such as tweezers, wire cutters, and a magnifying glass. Tweezers are indispensable for handling small components, while wire cutters assist in trimming excess leads after soldering. A magnifying glass can greatly improve your precision, allowing you to inspect solder joints closely for any potential issues.
Tips: When using tweezers, opt for anti-static versions to prevent damage to electronic parts. Keep your workspace organized with small containers for screws and components to streamline the assembly process.
Navigating the Printed Board Assembly (PBA) process can be daunting for beginners, but by following a structured, step-by-step approach, it becomes manageable. First, it is essential to start with a solid understanding of the design files and specifications of your printed circuit board (PCB). Review the schematic and layout to ensure that all components are correctly specified and placed. This step involves verifying the design rules and confirming that the design meets the required electrical and mechanical specifications before proceeding to assembly.
Next, choosing the right assembly method is crucial. Beginners can either opt for manual assembly or automated processes, depending on the project scale and complexity. For small runs or prototypes, manual assembly offers hands-on insights into component placement and soldering techniques. Alternatively, for larger volumes, automated assembly can streamline the process, reducing time and minimizing errors. Once the assembly method is decided, preparing the necessary tools, including solder, soldering iron, and cleaning materials, sets the stage for successful soldering and component integration.
As the assembly proceeds, maintaining an organized workflow is vital. This includes keeping track of component placement, ensuring correct soldering practices, and conducting regular inspections throughout the process. After assembly, thorough testing methods such as visual inspections, continuity tests, and functional tests are essential to verify that the board operates as intended. By following these systematic steps, beginners can successfully navigate the PBA process and build their confidence in printed circuit board assembly.
Navigating the printed board assembly (PBA) process can be daunting for beginners, given the myriad of challenges that come with it. One common issue is component misalignment during the placement phase. This can lead to poor solder joints, resulting in unreliable circuit functionality. To combat this, beginners should invest in practice setups that allow for hands-on learning with alignment tools and techniques to improve accuracy.
Another challenge is the tendency to overlook thermal management. Overheating can damage components or lead to performance issues. Beginners should consider the thermal characteristics of both the PCB material and the components being used. They can implement heat sinks or thermal pads where necessary to mitigate these risks.
**Tips:** Ensure that your work area is organized and that you have all necessary tools readily available before starting the assembly. This will help you to work more efficiently and reduce the chances of errors. Additionally, take time to familiarize yourself with the assembly process through online tutorials or workshops. Engaging with a community of fellow beginners or industry professionals can provide valuable insights and support.

Quality control in the printed board assembly (PBA) process is crucial for ensuring the reliability and performance of electronic products. According to a report from IPC, nearly 30% of failures in electronic devices arise from assembly-related issues, highlighting the importance of stringent quality measures. For beginners navigating this process, implementing best practices can dramatically reduce defects and increase the overall yield of assemblies.
One effective strategy is to adopt a robust inspection protocol. The use of Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) systems has become a standard practice in the industry, allowing for real-time detection of defects such as misalignments, soldering issues, or component placement errors. Reports indicate that integrating AOI can improve defect detection rates by up to 90%, significantly lowering the risks of product returns and enhancing customer satisfaction. Additionally, meticulous documentation of every stage of the assembly process is vital. This practice not only ensures traceability but also helps identify recurring problems, enabling teams to implement corrective actions swiftly.
Another key component of quality control in PBA is regular process audits. Research conducted by the IEEE shows that organizations that commit to regular audits and performance reviews see a 15-20% increase in operational efficiency. These audits provide insights into training needs, process bottlenecks, and equipment performance, thus fostering a culture of continuous improvement. By focusing on these best practices, beginners can lay a strong foundation for high-quality printed board assembly, ensuring they meet industry standards and customer expectations.